Synergetic effects of thymoquinone-loaded porous PVPylated Fe3O4 nanostructures for efficient pH-dependent drug release and anticancer potential against triple-negative cancer cells†
Abstract
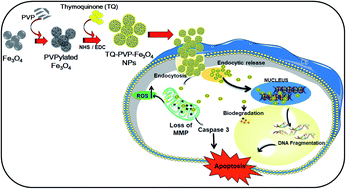
Porous iron oxide nanostructures have attracted increasing attention due to their potential biomedical applications as nanocarriers for cancer and many other therapies as well as minimal toxicity. Herbal anti-cancer agent thymoquinone loaded on Fe3O4 nanoparticles is envisaged to offer solution towards cancer treatment. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the efficacy of thymoquinone-loaded PVPylated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles (TQ-PVP-Fe3O4 NPs) against triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells. The porous PVPylated Fe3O4 NPs were prepared by a simple solvothermal process, whereas the thymoquinone drug was loaded via the nanoprecipitation method. Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic analysis confirmed the molecular drug loading, and surface morphological observation further confirmed this. The quantity of thymoquinone adsorbed onto the porous PVPylated Fe3O4 NPs was studied by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The positive surface charge of TQ-PVP-Fe3O4 NPs facilitates the interaction of the NPs with cancer (MDA-MB-231) cells to enhance the biological functions. In addition, the anticancer potential of NPs involving cytotoxicity, apoptosis induction, reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, and changes in the mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) of TNBC cells was evaluated. TQ-PVP-Fe3O4 NP-treated cells effectively increased the ROS levels leading to cellular apoptosis. The study shows that the synthesized TQ-PVP-Fe3O4 NPs display pH-dependent drug release in the cellular environment to induce apoptosis-related cell death in TNBC cells. Hence, the prepared TQ-PVP-Fe3O4 NPs may be a suitable drug formulation for anticancer therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...