Ecofriendly ruthenium-containing nanomaterials: synthesis, characterization, electrochemistry, bioactivity and catalysis†
Abstract
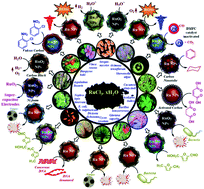
Among transition metals, ruthenium being an in-demand element along with its complexes with multidimensional applications in biology, catalysis (especially photocatalysis), and several other aspects of industrial materials, is lacking regards for the potential aspect of its nanoparticles. In the modern synthetic scenario, green synthesis of novel ruthenium nanoparticles for the development of novel materials with potential applications has become a focus. Ru-containing nanomaterials (Ru-cNMs) combined with metals like platinum and palladium or with non-metals like phosphorus and oxygen have shown applications as an anticancer, antimicrobial, and antioxidant agents along with wide-ranging catalytic applications. Reduction of Ru salts using biomaterials including plants etc. has emerged enabling the synthesis of Ru-cNMs. In this context, authors realize that poor availability of literature in this area of research seems to be one of the major handicaps that perhaps could be limiting its attractiveness to researchers. Therefore, it was thought worthwhile to present a review article to encourage, guide, and facilitate scientific researches in green ruthenium nanochemistry embodying synthesis, characterization and biological as well as catalytic applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...