Targeting prenylation inhibition through the mevalonate pathway
Abstract
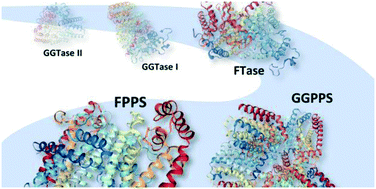
Protein prenylation is a critical mediator in several diseases including cancer and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Therapeutic intervention has focused primarily on directly targeting the prenyltransferase enzymes, FTase and GGTase I and II. To date, several drugs have advanced to clinical trials and while promising, they have yet to gain approval in a medical setting due to off-target effects and compensatory mechanisms activated by the body which results in drug resistance. While the development of dual inhibitors has mitigated undesirable side effects, potency remains sub-optimal for clinical development. An alternative approach involves antagonizing the upstream mevalonate pathway enzymes, FPPS and GGPPS, which mediate prenylation as well as cholesterol synthesis. The development of these inhibitors presents novel opportunities for dual inhibition of cancer-driven prenylation as well as cholesterol accumulation. Herein, we highlight progress towards the development of inhibitors against the prenylation machinery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...