A nanoscale, biocompatible and amphiphilic prodrug of cabazitaxel with improved anticancer efficacy against 3D spheroids of prostate cancer cells†
Abstract
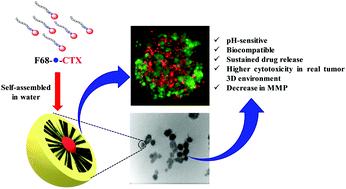
Chemotherapy is still a major therapeutic approach for the treatment of cancer. Cabazitaxel (CTX) is a highly effective anticancer drug for the treatment of prostate cancer. However, insolubility in water and non-specific drug delivery are major challenges in its application. In this study, we have designed pH-responsive and water-soluble prodrugs of CTX using pluronic F68 and pH-sensitive linkers for its site-specific delivery. The synthesized pluronic F68–CTX conjugates (F68–SA–CTX via a succinoyl linker; and F68–CAA–CTX via a cis-aconityl linker) were characterized through 1H-NMR and FTIR analysis. The nanomicelles of the amphiphilic prodrugs of CTX were self-assembled in water and demonstrated a low critical micelle concentration, a particle size of about 95 nm, monodispersity, spherical shape, and pH-responsive stability. Comparatively, cis-aconityl linker-based nanomicelles exhibited better pH-responsiveness and control over the release of CTX in comparison to succinoyl linker-based nanomicelles. Furthermore, the cis-aconityl linked nanomicelles showed greater inhibition of growth of human prostate cancer cells, stimulated higher ROS generation, decreased mitochondrial membrane potential and induced greater apoptosis without changing the cell cycle arrest mechanism of CTX. Thus, the present prodrug formulation of CTX is more advantageous than its conventional formulation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...