Nondestructive quantification of single-cell nuclear and cytoplasmic mechanical properties based on large whole-cell deformation†
Abstract
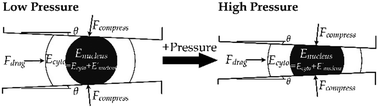
The mechanical properties of cell nuclei have been recognized to reflect and modulate important cell behaviors such as migration and cancer cell malignant tendency. However, these nuclear properties are difficult to characterize accurately using conventional measurement methods, which are often based on probing or deforming local sites over a nuclear region. The corresponding results are sensitive to the measurement position, and they are not decoupled from the cytoplasmic properties. Microfluidics is widely recognized as a promising technique for bioassay and phenotyping. In this report, we develop a simple and nondestructive approach for the single-cell quantification of nuclear elasticity based on microfluidics by considering different deformation levels of a live cell captured along a confining microchannel. We apply two inlet pressure levels to drive the flow of human nasopharyngeal epithelial cells (NP460) and human nasopharyngeal cancerous cells (NPC43) into the microchannels. A model considering the essential intracellular components (cytoplasm and nucleus) for describing the mechanics of a cell deforming along the confining microchannel is used to back-calculate the cytoplasmic and nuclear properties. On the other hand, we also apply a widely used chemical nucleus extraction technique to examine its possible effects (e.g., reduced nuclear modulus and reduced lamin A/C expression). To determine if the decoupled nuclear properties are representative of cancer-related attributes, we classify the NP460 and NPC43 cells using the decoupled physical properties as classification factors, resulting in an accuracy of 79.1% and a cell-type specificity exceeding 74%. It should be mentioned that the cells can be recollected at the device outlet after the nondestructive measurement. Hence, the reported cell elasticity measurement can be combined with downstream genetic and biochemical assays for general cell research and cancer diagnostic applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...