Silicon isotope measurement in zircon by laser ablation multiple collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry†
Abstract
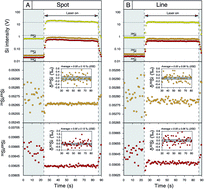
This study reports the first Si isotope data measured in zircon using nanosecond laser ablation multiple collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Long-term (>2 years) external reproducibility obtained on the 91500 zircon standard is 0.13‰ and 0.21‰ (2SD) for δ29Si and δ30Si (per mil deviation from the quartz reference NBS 28), respectively, and typical precision on a single run is on the order of 0.10‰ and 0.12‰ (2SE) for δ29Si and δ30Si, respectively. Our results show good consistency between laser ablation multiple collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-MC-ICP-MS) and solution multiple collector inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (S-MC-ICP-MS)/secondary ionization mass spectrometry (SIMS) data demonstrating that the Si isotopic composition of zircon can be accurately measured by LA-MC-ICP-MS. Obtained δ30Si values on natural zircon standards range from −0.32 ± 0.23‰ (2SD) for 91500 to −0.47 ± 0.17‰ for MudTank, whereas the MUN (synthetic) zircon standards have lower δ30Si values around −2.0‰ (e.g. −2.08 ± 0.17‰ for MUN-1-2b). Silicon isotope measurements by LA-MC-ICP-MS open new possibilities for studying zircon formation in various geological contexts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...