Quantitative trace elemental analysis by laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy with dried droplet pretreatment
Abstract
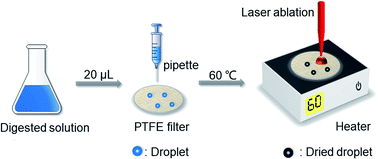
Quantitative trace element analysis is crucial to a range of industries, including food, natural and man-made materials, and biomedicine. For this purpose, we here developed laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) with dried droplet sample pretreatment. This novel method is quantitative and especially suited to analyzing small solid samples with trace concentrations of low atomic number elements. The dried droplet pretreatment involves acid digesting the sample and allowing a droplet to dry on filter paper free of the analytes. LIBS was then performed on the dried droplet using pulsed laser ablation and spectroscopic detection from 200–1000 nm with 0.1 nm resolution. A standard addition approach was employed to quantify LIBS signals by adding known amounts of analytes into the droplets. The method was demonstrated by measuring sodium, potassium and calcium in four selected samples. All the standard addition calibration curves showed good linearity, with all regression coefficients >0.981 and relative standard deviation <5.6%. Meanwhile, the limit of detection ranges from 0.57 to 14.5 mg kg−1 and the limit of quantification ranges from 1.9 to 48 mg kg−1. For validation, all samples were also analyzed by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). The relative error of LIBS compared to ICP-MS was low, <6.3% for all samples. Altogether, LIBS with dried droplet pretreatment is a promising new technique for quantitative trace element analysis of small solids.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...