Rapid determination of lead isotopes in water by coupling DGT passive samplers and MC-ICP-MS laser ablation†
Abstract
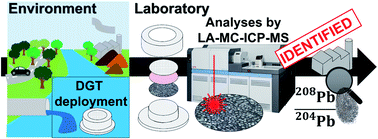
Despite a considerable reduction in the amount of lead (Pb) in the environment as a result of control measures and policies, environmental Pb exposure remains a major public-health issue. Using Pb isotopes is a powerful tool for tracking metal pollution in the environment, especially in natural water where—even at low concentrations—it can have negative health effects. We developed a new method of combining a commercially available chelex 100-DGT passive sampler and MC-ICP-MS laser ablation for measuring Pb-isotope compositions in natural water. This combination offers several advantages: (1) the DGT device samples an isotopic composition of natural water integrated over time and pre-concentrates metals in situ. (2) Laser ablation allows a direct analysis of DGT without chemical preparation, reducing preparation time and the risk of contamination. We used a low fluence (3.06 J cm−2) for linear ablation of squares with 150 μm sides, achieving optimal sensitivity without burning the sample. A good compromise between pulse-repetition rate (Hz) and scan speed (μm s−1) is necessary for obtaining good sensitivity with similar intensity on both standard and sample, while maintaining a low background level. For an accurate analysis of the Pb-isotope composition of DGT by LA-ICP-MS a matrix-matched calibration is necessary, which was easily produced by immersing DGT in a standard solution. Finally, a water-flow experiment in a column demonstrated that it possible to analyse Pb-isotope compositions in water by DGT and MC-ICP-MS laser ablation with sufficient precision (0.09% for 207Pb/206Pb) for distinguishing various anthropogenic Pb sources in the environment. This method offers new perspectives for public policy development as it facilitates isotopic monitoring of natural water, better to combat Pb pollution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...