Investigation of the multi-elemental self-absorption mechanism and experimental optimization in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy
Abstract
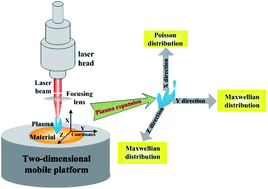
The self-absorption effect reduces the accuracy of element measurements in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) experiments. In this paper, the mechanism of the self-absorption effect was studied. First, we established a plasma concentration distribution model and plasma dynamics model of the plasma expansion in three directions during LIBS based on physical laws. By coupling a plasma concentration distribution model with a self-absorption model, the LIBS self-absorption effect value model was obtained. Second, the models were applied in a numerical simulation to determine plasma spatial distribution characteristics during LIBS. The self-absorption effect values of spectral lines were calculated. Finally, experiments were conducted with an optical spectrometer to obtain the Na, K, and Al atomic emission spectra. On the theoretical plane, the Boltzmann plot method and the Stark broadening method were used to obtain the plasma characteristic parameters. The spectral line intensities of the Na, K and Al atom lines were obtained without and with microwave-assisted LIBS experiments for comparison. The experimental analysis showed that during the LIBS process, microwave assistance can enhance the emission spectroscopy intensity and inhibit or reduce the LIBS self-absorption effect. The experimental samples were in good agreement with those of theoretical simulation, indicating the effectiveness and practicability of the created LIBS self-absorption effect value model, which can improve the optimization of the LIBS process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...