Improved measurement in quantitative analysis of coal properties using laser induced breakdown spectroscopy
Abstract
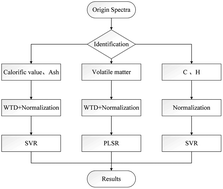
It is of great significance to realize the rapid or online analysis of coal properties for optimization of combustion in thermal power plants. In this work, a set of calibration schemes based on laser induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS) was determined to improve the measurements in quantitative analysis of coal properties, including proximate analysis (calorific value, ash, volatile content) and ultimate analysis (carbon and hydrogen). Firstly, different normalization methods (channel normalization and normalization over the whole spectral area) combined with two regression algorithms (partial least squares regression [PLSR] and support vector regression [SVR]) were compared to make an initial selection of the appropriate calibration method for each indicator. Then, the influence of de-noising by wavelet threshold de-noising (WTD) on quantitative analysis was further studied, whereby the final analysis schemes for each indicator were determined. The results showed that WTD coupled SVR can make a good estimate of calorific value and ash: the root mean square errors of prediction (RMSEP) were 0.80 MJ kg−1 and 0.60%. Coupling of WTD and PLSR performed best for the measurement of volatile content, and the RMSEP was 0.76%. For the quantitative analysis of carbon and hydrogen, normalization over the whole spectral area combined with SVR can get better measurement results, and the RMSEP of the measurements were 1.08% and 0.21%, respectively. The corresponding average standard deviations (RSD) for calorific value, ash, volatile content, carbon and hydrogen of the validation sets were 0.26 MJ kg−1, 0.57%, 0.79%, 0.47% and 0.08%, respectively. The results demonstrated that the selection of appropriate spectral pre-processing coupled with calibration strategies for each indicator can effectively improve the accuracy and precision of measurements of coal properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...