Evidences of starch–microwave interactions under hydrolytic and pyrolytic conditions†
Abstract
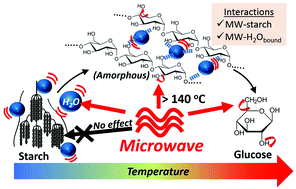
Microwaves (MWs) are promising technologies for energy-efficient biorefineries which reduce our dependence on petroleum. Here we present evidence for the first time of important interactions between MW and starch, a major biomass from massive global food wastes, which can be observed under both hydrolytic and pyrolytic conditions. Starch is transformed into disordered fractions at elevated temperatures, in which the functional groups gained higher degree of freedom serving as MW radiators to facilitate thermochemical depolymerization. In addition, starch retains water molecules in the hydrogen bonding network during gelatinization, which enables frictional heat generation via dipolar polarization of the bound water. This provokes the MW superheating of starch gel that is superior to pure water with declining dielectric loss in high-temperature region (>140 °C). As a result of self-improved dielectric heating, MW-assisted hydrolysis consumes 47% less energy to achieve similar total product yields from the starch depolymerization compared to conventional conductive heating. The findings improve our understanding of how MW participates in multi-phasic heterogenous systems and propose a starch-initiated superheating mechanism, which are important to help us maximize the advantageous effects of MW in biorefineries of complex biomass feedstocks.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...