Sterically driven metal-free oxidation of 2,7-di-tert-butylpyrene†
Abstract
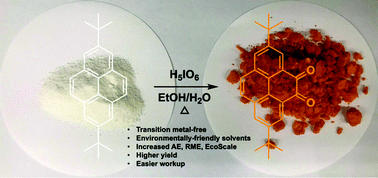
We disclose an unprecedented single-step metal-free green oxidation of 2,7-di-tert-butylpyrene selectively into either the corresponding 4,5-dione or 4,5,9,10-tetraone, two key building blocks used for organic optoelectronic applications using hypervalent iodine oxyacids. This new method results in dramatic improvements in terms of yield, selectivity (dione vs. tetraone), ease of workup, cost and toxicity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...