A sustainable synthetic route for biobased 6-hydroxyhexanoic acid, adipic acid and ε-caprolactone by integrating bio- and chemical catalysis†
Abstract
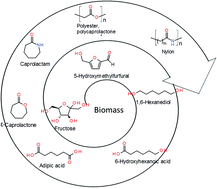
A green route for the production of 6-carbon polymer building blocks 6-hydroxyhexanoic acid, adipic acid and ε-caprolactone from 1,6-hexanediol, a hydrogenation product of biobased 5-hydroxymethylfurfural is reported. Gluconobacter oxydans oxidized 1,6-hexanediol completely to adipic acid, and selectively at pH 6–7 to 6-hydroxyhexanoic acid, which was converted to ε-caprolactone by catalytic cyclization.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...