High enhancement of the hydrolysis rate of cellulose after pretreatment with inorganic salt hydrates
Abstract
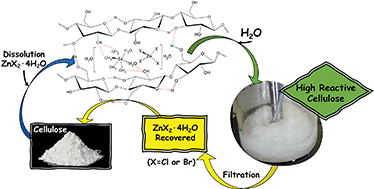
We study the use of inorganic salt hydrates as solvents in the dissolution/precipitation pretreatment of cellulose. The dissolution of cellulose was very fast (15 min in some cases) at the low temperature of 70 °C. ZnCl2·4H2O, ZnBr2·4H2O, LiCl·8H2O and LiBr·4H2O were studied as solvent. The dissolution/precipitation process dramatically modified the cellulose structure, which was completely deconstructed, as corroborated by both XRD and SEM. The nature of these salts affects cellulose dissolution. The change in cellulose morphology after dissolution/precipitation pretreatment produced an increase in the rate of hydrolysis with respect to that of untreated cellulose. The acidic catalyst employed in hydrolysis had a moderate effect on the reaction results. The best performance was obtained with H4SiW12O40 (0.05 M) at 140 °C for 300 min, where the cellulose conversion was close to 99% and the glucose yield was 90%.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...