Hierarchical porous carbon derived from the gas-exfoliation activation of lignin for high-energy lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
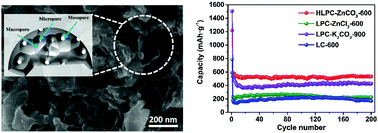
A large scale hierarchical porous carbon material was developed via a cheap and environmentally friendly activation approach using the most abundant aromatic polymer in plants, lignin, and ZnCO3 as a non-corrosive and recyclable activator. The three-dimensional (3D) novel hierarchical lignin-derived porous carbon (HLPC) possesses a desirable microstructure and a large number of mesopores. This structure is achieved by activation from the gas released by ZnCO3, i.e., the gas-exfoliation of lignin and nano-sized ZnO particles (10–20 nm) in situ generated from ZnCO3 have an in situ templating effect. As a result, the resulting HLPC simultaneously achieved excellent volume/mass energy density (730 mA h·cm−3/550 mA h·g−1 after 200 cycles at 0.2 A·g−1) with excellent cycling performance (∼99% retention after 10 000 cycles). In particular, the volume capacitances obtained in our work are the highest among the reported lignin-based carbon materials. Compared to conventional activators, ZnCO3 as a green, non-corrosive, low-cost and recyclable activator has broad prospects in the preparation of biomass-based carbon materials. Our work demonstrates the successful and large-scale conversion of industrial lignin into a high-performance carbon-based material, and the promising mass/volumetric performance further suggests that the method developed may provide an accessible pathway for improving the energy density of energy storage materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...