Production of chiral alcohols from racemic mixtures by integrated heterogeneous chemoenzymatic catalysis in fixed bed continuous operation†
Abstract
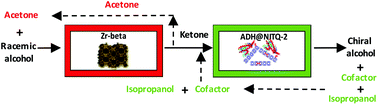
Valuable chiral alcohols have been obtained from racemic mixtures with an integrated heterogeneous chemoenzymatic catalyst in a two consecutive fixed catalytic bed continuous reactor system. In the first bed the racemic mixture of alcohols is oxidized to the prochiral ketone with a Zr-Beta zeolite and using acetone as the hydrogen acceptor. In the second catalytic bed the prochiral ketone is stereoselectively reduced with an alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) immobilized on a two dimensional (2D) zeolite. In this process, the alcohol (isopropanol) formed by the reduction of acetone in the first step reduces the cofactor in the second step, and the full reaction cycle is in this way internally closed with 100% atom economy. A conversion of about 95% with ∼100% selectivity to either the (R) or the (S) alcohol has been obtained for a variety of racemic mixtures of alcohols.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...