Catalyst-free vitrimer elastomers based on a dimer acid: robust mechanical performance, adaptability and hydrothermal recyclability†
Abstract
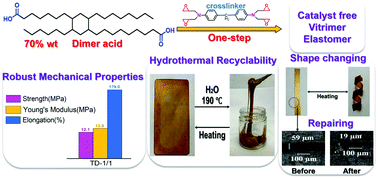
Vegetable oil (VO) derivatives as feedstocks for elastomeric materials have been extensively studied. However, most of the resulting materials generally exhibit poor mechanical performance and lack reparability and recyclability due to the irreversible nature of the crosslink network. To address these issues, in this work, a VO-based vitrimer elastomer is prepared by curing of a VO-derived dimer acid (DA) and a tetrafunctional glycidylamine epoxy (TGDDM). DA accounts for 65–77 wt% of the elastomer materials. When the molar ratio of epoxy to –COOH is 1/1, the prepared elastomer exhibits a tensile strength of 12.1 MPa and an elongation at break of 179.0% which are comparable to those of commercial elastomers and superior to those of VO-based elastomers reported in the literature. The elastomers prepared display self-repairing and shape changing properties at elevated temperatures (>170 °C) due to the thermally induced dynamic transesterification reaction (DTER) in the network structure. Unlike most other vitrimer networks based on ester linkages that require a significant amount of catalyst, this network contains abundant tertiary amines originated from TGDDM and is self-catalytic. In addition, the elastomer is degradable in water at above 170 °C without using any catalyst. This is because the tertiary amines originally from TGDDM catalyze the hydrolysis of the ester bonds of the elastomer. The degraded product is repolymerizable to give new crosslinked elastomers. This work presents a simple and feasible method for the preparation of a VO-based vitrimer elastomer that is readily pluggable into current elastomer manufacturing and may cause a significant impact on the rubber industry.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...