Ethyl acetate as solvent for the synthesis of poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline)†
Abstract
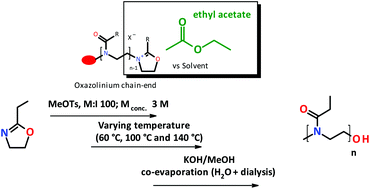
Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) (PEtOx) is the most common poly(2-oxazoline) for biomedical applications resulting from its high water-solubility, good commercial availability and well-controlled polymerization. In this article, we report the polymerization of 2-ethyl-2-oxazoline (EtOx) in ethyl acetate to replace the current state-of-the-art polymerization of EtOx in acetonitrile and chlorobenzene. This switch towards ethyl acetate as green solvent is an important improvement towards pharmaceutical compliance/compatibility, besides the lower burden for the environment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...