Metagenomics approach to the intestinal microbiome structure and function in high fat diet-induced obesity in mice fed with conjugated linoleic acid (CLA)
Abstract
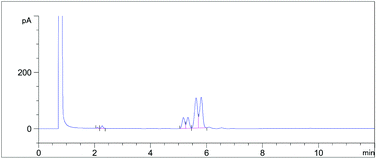
In this study, a high fat diet induced obesity mouse model (DIO) was used to investigate the modulatory effect of high purity conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) on the intestinal microbiota. CLA was prepared by a simulated moving bed chromatography system and its influence on the gut microbes was analyzed by 16S amplicon V3–V4 region analysis. We observed a significant increase in the bacterial biodiversity and the abundance of genera of butyrate- and acetate-producing bacteria. After taking CLA for 6 weeks, the abundance of Bacteroides in the intestines of mice greatly increased, while the abundance of Firmicutes decreased. The corresponding decrease in the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio reflected a positive modulatory effect of CLA on the intestinal microbiota. In addition, KEGG pathways for the nucleotide metabolism, metabolism of terpenoids and polyketides and lipid metabolism were among the most differentially expressed genes after CLA intervention. The current study revealed that CLA can be used as a functional food component with potential therapeutic value to prevent obesity-related metabolic disorders by manipulating the intestinal microbiota.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...