Design of polymer-free Vitamin-A acetate/cyclodextrin nanofibrous webs: antioxidant and fast-dissolving properties†
Abstract
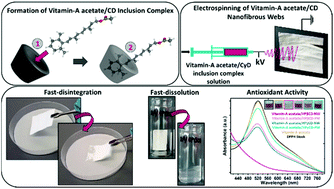
The encapsulation of food/dietary supplements into electrospun cyclodextrin (CD) inclusion complex nanofibers paves the way for developing novel carrying and delivery substances along with orally fast-dissolving properties. In this study, CD inclusion complex nanofibers of Vitamin-A acetate were fabricated from polymer-free aqueous systems by using the electrospinning technique. The hydroxypropylated (HP) CD derivatives of HPβCD and HPγCD were used for both encapsulation of Vitamin-A acetate and the electrospinning of free-standing nanofibrous webs. The ultimate Vitamin-A acetate/CD nanofibrous webs (NWs) were obtained with a loading capacity of 5% (w/w). The amorphous distribution of Vitamin-A acetate in the nanofibrous webs by inclusion complexation and the unique properties of nanofibers (e.g. high surface area and porosity) ensured the fast disintegration and fast dissolution/release of Vitamin-A acetate/CD-NW in a saliva simulation and aqueous medium. The enhanced solubility of Vitamin-A acetate in the case of Vitamin-A acetate/CD-NW also ensured an improved antioxidant property for the Vitamin-A acetate compound. Moreover, Vitamin-A acetate thermally degraded at higher temperature in Vitamin-A acetate/CD-NWs, suggesting the enhanced thermal stability of this active compound. Here, HPβCD formed inclusion complexes in a more favorable way when compared to HPγCD. Therefore, there were some uncomplexed Vitamin-A acetate crystals detected in Vitamin-A acetate/HPγCD-NW, while Vitamin-A acetate molecules loaded in Vitamin-A acetate/HPβCD-NW were completely in complexed and amorphous states. Depending on this, better solubilizing effect, higher release amount and enhanced antioxidant properties have been provided for the Vitamin-A acetate compound in the case of Vitamin-A acetate/HPβCD-NW.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...