Iron-induced peroxidation of trilinolein nano-emulsions under model gastric conditions and its inhibition by dietary phenolic antioxidants†
Abstract
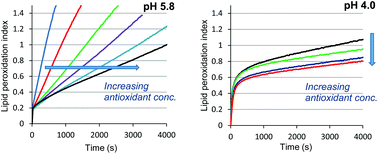
An early mechanism for the health benefits of dietary plant phenols is their antioxidant activity in the upper digestive tract. Indeed, these non-essential micronutrients abundant in fruits and vegetables can efficiently fight the iron-induced peroxidation of dietary lipids in the gastric compartment, a recognized form of postprandial oxidative stress. In this work, this phenomenon is investigated through a simple model based on nano-emulsions of trilinoleylglycerol, which permits a direct spectroscopic monitoring and mechanistic insights sustained by extensive kinetic analysis. Polyphenols belonging to the main dietary classes are tested, in particular, flavonols, anthocyanins, flavanols and oligomeric procyanidins. Overall, the common polyphenols tested are good inhibitors of lipid peroxidation induced by metmyoglobin (heme iron) in the early stage of digestion (pH 5–6). For instance, under our peroxidation conditions (2 μM heme, 0.7 mM linoleic acid equivalent, 4.5 mM Brij®35), IC50 concentrations in the range 0.4–1.9 μM were estimated for the set of polyphenols, with oligomeric procyanidins being less inhibitory than the flavanol monomers. However, the polyphenols are ineffective at lower pH (pH 4) when the hematin cofactor is dissociated from its protein (globin). On the other hand, a moderate protection against lipid peroxidation induced by free iron (e.g., released by the oxidative degradation of hematin) persists. This protocol, which combines simplicity and nutritional relevance, could provide a basis for standard tests aimed at assessing the antioxidant capacity of foods and food additives.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...