Encapsulation of Lactobacillus acidophilus NCDC 016 cells by spray drying: characterization, survival after in vitro digestion, and storage stability
Abstract
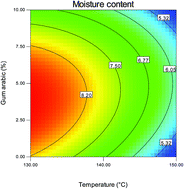
In the present study, probiotic cells (Lactobacillus acidophilus) were encapsulated by spray drying technology to produce a probiotic powder using 20% maltodextrin and varied concentrations of gum arabic. The effects of processing conditions such as inlet air temperature (130–150 °C) and gum arabic concentration (0–10%) on the encapsulation efficiency, physical properties, and morphology were studied. For all the tested formulae, the moisture content, water activity, encapsulation efficiency, hygroscopicity, and wettability obtained were in the range of 4.59–9.05% (w.b.), 0.33–0.52, 65–89.15%, 12 to 21.15 g H2O per 100 g dry weight, and 116 s to 353 s, respectively. The Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) results have shown that gum arabic and maltodextrin show structural stability during spray drying. The encapsulated probiotic cells exhibited better viability of 4.03, 4.68, and 5.34 log CFU g−1 after 3 h of exposure to a simulated gastric fluid (SGF) solution at pH levels of 1, 1.5, and 2, respectively, compared to free cells. The viability of encapsulated cells stored for 12 weeks under refrigerated conditions (4 °C) and at room temperature (25 °C) was found to be 6.05 log CFU g−1 and 1.24 log CFU g−1, respectively.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...