The exogenous natural phospholipids, EPA-PC and EPA-PE, contribute to ameliorate inflammation and promote macrophage polarization†
Abstract
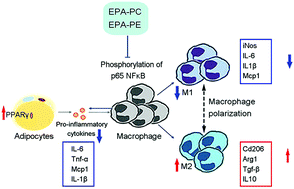
Dietary intake of sea cucumber phospholipids, a rich source of eicosapentaenoic acid in the form of phospholipids (EPA-PLs), has been shown to improve obesity and related disorders. However, whether dietary eicosapentaenoic acid in the form of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine (EPA-PC and EPA-PE, respectively) shows anti-inflammatory efficacy and its underlying mechanism has scarcely been investigated to date. Thus, the purpose of this study was to determine if EPA-PC and EPA-PE improve chronic inflammation and alter the interaction between macrophages and adipocytes. We found that EPA-PC and EPA-PE reduced the elevated levels of serum TNF-α, IL-6 and MCP1 and attenuated macrophage infiltration in the liver and iWAT of an HFSD-induced inflammatory model. Importantly, EPA-PC and EPA-PE promoted macrophage polarization in white adipose tissue. Furthermore, this effect on macrophage polarization was also observed in a 3T3L1 and Raw 264.7 Transwell co-culture system, which suggests that EPA-PC and EPA-PE attenuate chronic inflammation by promoting the M2-dominant polarization of macrophages in vitro. Our experiments in vitro illustrated that EPA-PC and EPA-PE attenuated the phosphorylation of p65 NFκB in Raw264.7 macrophages and increased PPARγ expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes during the co-culture, which may contribute to the improvement in adipose inflammation. Thus, dietary eicosapentaenoic acid in the form of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine may be a therapeutic strategy for chronic inflammation in obese adipose tissue.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...