Caenorhabditis elegans as an in vivo model to assess fucoidan bioactivity preventing Helicobacter pylori infection
Abstract
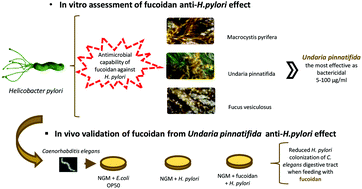
Currently, Helicobacter pylori is the unique biological carcinogenic agent. The search for antimicrobial alternatives to antibiotics against this pathogen has been categorized as a priority due to the drastic failure associated with current applied antibiotic therapy. The present study assessed the bioactive antimicrobial capability of fucoidan (“Generally Recognized as Safe” approval – European Commission December 2017) from different species of Phaeophyceae algae (Fucus vesiculosus, Undaria pinnatifida, Macrocystis pyrifera) against H. pylori. All the studied fucoidans showed bacteriostatic and bactericidal effects at the studied concentrations [5–100] μg ml−1 and exposure times [0–7 days]. The most effective anti-H. pylori fucoidan was validated in Caenorhabditis elegans as an in vivo model. C. elegans feed was supplemented with Undaria pinnatifida [0–100] μg ml−1 fucoidan, resulting in a significant improvement in lifespan, lowered H. pylori concentration in the digestive tract, and increased egg-laying pattern. New research lines proposing this compound as an active agent in nutraceutical and preventive novel therapies should be opened.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...