Comparison of the effects of resveratrol and its derivative pterostilbene on hepatic oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in piglets challenged with diquat†
Abstract
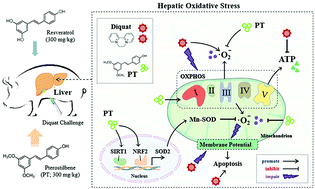
This study investigated the potential of resveratrol (RSV) and its derivative pterostilbene (PT) to prevent diquat (DQ)-induced hepatic oxidative damage and mitochondrial dysfunction in piglets. Seventy-two weanling piglets were randomly divided into the following treatment groups: non-challenged control group, DQ-challenged control group, and DQ-challenged groups supplemented with either 300 mg RSV per kg of diet or an equivalent amount of PT. Each treatment group consisted of six replicates with three piglets per replicate (n = 6). After a two-week feeding trial, piglets were intraperitoneally injected with either 10 mg DQ per kg of body weight or sterile saline. At 24 hours post-injection, one piglet from each replicate (six piglets per treatment) was randomly selected for sample collection and biochemical analysis. Compared with the DQ-challenged control group, PT attenuated the growth loss of piglets after the DQ challenge (P < 0.05). Administration of PT was more effective than its parent compound in inhibiting the DQ-induced hepatic apoptosis and the increased generation of total cholesterol, superoxide anion, and lipid peroxidation products (P < 0.05). Specifically, PT facilitated nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 signals and the expression and activity of manganese superoxide dismutase, while it also prevented mitochondrial swelling, membrane potential collapse, and adenosine triphosphate depletion, possibly through the activation of sirtuin 1 (P < 0.05). These results indicate that PT may be superior to RSV as an antioxidant to protect the liver of young piglets from oxidative insults.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...