The influence of oil composition on the transformation, bioaccessibility, and intestinal absorption of curcumin in nanostructured lipid carriers†
Abstract
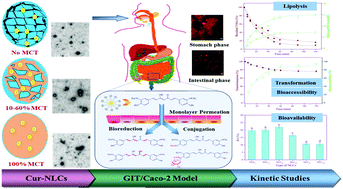
In this study, the influences of liquid medium-chain triglyceride (MCT) and solid glyceryl tristearate (GTS) contents in the lipid matrix of nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) on their delivering capacities with respect to curcumin (Cur) were investigated by using a simulated gastrointestinal tract and Caco-2 monolayer models. The transformation of the encapsulated Cur decreased on increasing the MCT content in the lipid matrix of NLCs because it facilitated their lipolysis and promoted the exposure of Cur to a harsher exterior environment. Cur bioaccessibility was positively correlated with the level of micellized stearic acid resulting from GTS hydrolysis, which might be attributed to the fact that it could afford large hydrophobic domains to accommodate Cur. This value initially increased with an increase in the MCT content, reaching a maximum at 20% (w/w) and decreasing thereafter. The intestinal absorption of micellar Cur ranged from 26.06% to 38.76%, and a majority of the transported molecules were its reductive and conjugative metabolites. Overall, NLC containing 20% MCT in the lipid matrix afforded the highest Cur bioavailability, followed by that containing 10, 0, 40, 60, and 100% MCT. This work provides useful insights into the rational design of NLCs to optimize the bioavailability of the loaded agent.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...