Fucoxanthin alleviates palmitate-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 cells through improving lipid metabolism and attenuating mitochondrial dysfunction
Abstract
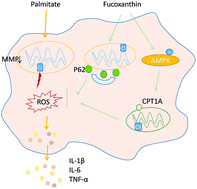
In this study, we aimed to examine the effects of fucoxanthin on inflammation triggered by palmitate in macrophages. Raw 264.7 cells were treated with palmitate with or without fucoxanthin co-treatment. Fucoxanthin greatly alleviated palmitate-induced decrease in cell viability and loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. Fucoxanthin also significantly attenuated the palmitate-induced transcriptional expression of Il-6, Il-1β, Tnfα and Nlrp3 inflammasomes and increased the expression of Tgfb. In addition, fucoxanthin decreased triglyceride accumulation induced by palmitate through enhancing the expression of Cpt1a, Pparg and other lipid metabolism genes. Inhibition of CPT1a by etomoxir attenuated the anti-inflammatory effect of fucoxanthin. Furthermore, fucoxanthin increased AMPK phosphorylation and AMPKa1 knockdown by its specific siRNA diminished protective function. In addition, fucoxanthin restored palmitate-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and improved mitophagy-related gene expression. These findings suggest that fucoxanthin could attenuate free fatty acid-induced inflammation in macrophages through modulating lipid metabolism and mitigating mitochondrial dysfunction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...