Citrus auraptene induces drug efflux transporter P-glycoprotein expression in human intestinal cells
Abstract
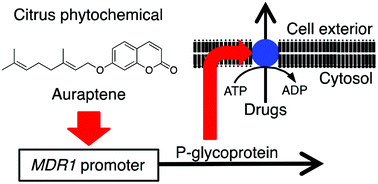
P-glycoprotein (encoded by MDR1) is a membrane transport protein expressed in the intestine, liver, kidney, placenta, and blood–brain barrier. It excludes various clinically important drugs from cells, such as verapamil, digoxin, tacrolimus, and vinblastine. Therefore, human P-glycoprotein plays important roles in drug absorption, distribution, and excretion. We reported previously that auraptene, a natural compound occurring widely in citrus fruit (e.g., grapefruit), inhibited P-glycoprotein-mediated drug transport. In this study, we investigated the effects of auraptene and other phenylpropanoids on P-glycoprotein expression using human intestinal epithelial LS174T cells and a reporter plasmid expressing 10.2 kbp of the upstream regulatory region of MDR1. Auraptene (7-geranyloxycoumarin), a prenylated coumarin, and several phenylpropanoids, such as 3-(4′-geranyloxy-3′-methoxyphenyl)-2-trans propenoic acid, derricidin [2′-hydroxy-4′-(prenyloxy)chalcone], and 3-(4′-geranyloxyphenyl)-propanoic acid, induced MDR1 promoter activity in LS174T cells. Overexpression of the nuclear receptor human pregnane X receptor gene (NR1I2) enhanced auraptene-induced MDR1 activation. Nuclear factor-kappaB inhibitors, Bay11-7082 and JSH-23, repressed MDR1 activation by auraptene. Western blot analyses showed the induction of P-glycoprotein expression in the auraptene-treated LS174T cells. The citrus phytochemical auraptene can induce the drug efflux transporter P-glycoprotein in human intestinal cells, and thus has the potential to cause food–drug interactions.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Food & Function Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...