Potential use of ellagic acid for endometriosis treatment: its effect on a human endometrial cell cycle, adhesion and migration
Abstract
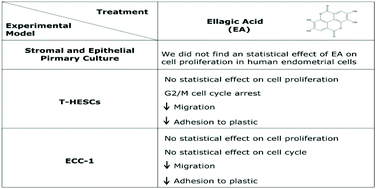
Endometriosis is a common and challenging condition of reproductive-aged women that is defined as the presence of endometrial-like tissue outside the uterine cavity. Despite its prevalence, there is still no effective therapeutics; so we aim to evaluate the ellagic acid (EA) effect on the most relevant aspects that are known to be altered in endometriosis. Endometrial primary cultures from women with and without endometriosis and endometrial cell lines were incubated with EA (50 and 100 μM) for 24 and 48 h. The results demonstrated that EA arrests an endometrial stromal cell cycle on the G2/M phase, after 48 h. In addition, 100 μM EA treatment significantly decreased ECC-1 cell migration at 20 h and T-HESC cell migration at 10 h and 20 h, while 50 μM EA significantly decreased T-HESC cell migration at 20 h. On the other hand, we proved that the treatment with EA for 24 h reduces T-HESC and ECC-1 adhesion to plastic. However, we did not find an effect of EA on cell proliferation. EA has an inhibitory effect on endometrial cell adhesion, migration and cell cycle progression in vitro. These highlight the idea to investigate natural compounds as novel and promising candidates for therapeutic treatment of endometriosis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...