Pterostilbene alleviates cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats by modulating microglial activation
Abstract
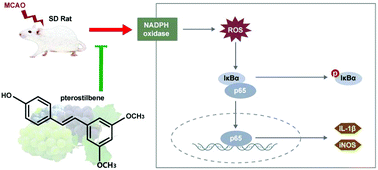
Ischemic stroke is a severe neurological disease without known effective therapy. Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation plays an important role in ischemic stroke. Therefore, finding a safe and effective microglial activation inhibitor might lead to an effective therapeutic strategy against ischemic stroke. In this project, our goal was to explore both the mechanism and effect of pterostilbene in MCAO/R rats. The potential effect of pterostilbene on ischemic stroke was tested using MCAO/R rats and its effect on microglial activation was tested in LPS-stimulated BV-2 cells. In vivo, pterostilbene decreased the neurological scores, brain water content and infarct volume in MCAO/R rats. Pterostilbene increased the number of mature neurons, decreased the number of activated microglia, and reduced iNOS and IL-1β mRNA expression. Pterostilbene inhibited phosphorylated-IκBα expression, thus promoting IκBα expression and inhibiting ROS overexpression. In vitro, pterostilbene inhibited the expression of inflammatory cytokines and suppressed NAPDH activity as well as activation of both the NF-κB pathway and ROS production. To our knowledge, our study is the first to demonstrate that pterostilbene-mediated alleviation of cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats may be correlated with the inhibition of the ROS/NF-κB-mediated inflammatory pathway in microglia, indicating the potential for the use of pterostilbene as a candidate therapeutic compound for ischemic stroke.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...