Girinimbine from curry leaves promotes gastro protection against ethanol induced peptic ulcers and improves healing via regulation of anti-inflammatory and antioxidant mechanisms†
Abstract
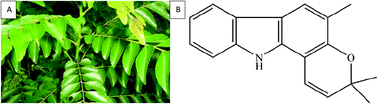
Curry leaves (Murraya koenigii) are a leafy spice used in Indian cookery for its fragrant aroma. Many bioactive functional compounds have been identified, and among them carbazole alkaloids have attracted wide attention due to their multi-dimensional medicinal value. Even though it has been established that the carbazole alkaloid is responsible for the anti-ulcer effect showed by this culinary herb, there is no further evidence to say which phytochemical is responsible for this. In the present study, we investigated the gastro-protective effects and mechanism of girinimbine, a major carbazole alkaloid present in curry leaves. Rats were administered with ethanol to produce gastric ulcers, and the prophylactic effect of girinimbine was evaluated. A macroscopic and histological examination was carried out to examine the lesions. Furthermore, the mucus production, NO production, PGE2 synthesis, mucosal nonprotein sulphydryls, glutathione (GSH) level, lipid peroxidation (MDA) level and COX inhibition were assessed. In addition, in particular, TNF-α and IL-6, two important cytokines, were evaluated. Immunohistochemical and gene expression studies were conducted to determine the HSP70 and iNOS biomarkers. Our results indicated that girinimbine significantly reduced the ulcer index and totally safeguarded the mucosa from lesions. The protective effect of girinimbine was complemented through the restoration of the reduced GSH and NP-SH level. This was associated with a reduction of MDA, which was elevated by the administration of ethanol. Pre-treatment of the ethanol induced ulcer with girinimbine reduced the NO concentration in the plasma and elevated PGE2 together with a decreased level of TNF-α and IL-6. Girinimbine had shown suppressing effects on COX-2 enzymes, but not on COX-1. In addition, significantly upregulated HSP70 and downregulated iNOS were observed in girinimbine treated rat tissue at both the transcriptional and translational level. Our results clearly indicated that girinimbine displayed a significant gastro-protection effect, via the capacity to inhibit inflammatory responses and antioxidant potential.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...