Purification, characterization and molecular cloning of a dicaffeoylquinic acid-hydrolyzing esterase from human-derived Lactobacillus fermentum LF-12†
Abstract
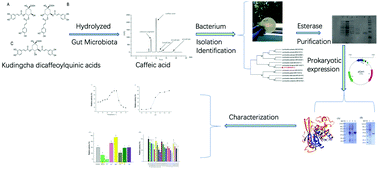
Dicaffeoylquinic acids (DiCQAs), the main components of kudingcha made from the leaves of Ilex kudingcha, could be transformed by gut microbiota. However, the information about the related microorganisms and enzymes involved in the biotransformation of DiCQAs in the human gut is limited. Therefore, a strain of bacteria that could hydrolyze DiCQAs, belonging to Lactobacillus fermentum named L. fermentum LF-12, was isolated from human feces in the present study. Furthermore, an esterase for the hydrolysis of DiCQAs was purified from L. fermentum LF-12 and heterogeneously expressed in Escherichia coli. The esterase could be induced to exert superior hydrolytic activity in the presence of lactose as the carbon source. The molecular weight of the purified esterase was determined to be 31.9 kDa, and the isoelectric point, optimal pH and temperature for the esterase were 4.71, 6.5 and 45 °C, respectively. The enzyme activity was improved by Mg2+ and Ca2+, and reduced by Co2+, Cu2+, EDTA and some kinds of organic solvents. The present results provide new insights into the metabolism of DiCQAs by the human gut.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...