Inducing secondary structural interplays between scallop muscle proteins and soy proteins to form soluble composites
Abstract
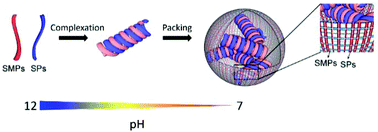
Developing food protein structures with the freedom to tune their internal molecular arrangements is a fascinating aspect for serving the demands of multifunctional food components. However, a protein's conformation is highly submissive to its amino acid sequences, posing a great limitation on controlling its structural rearrangements. In this study, based on simply co-dissolving scallop muscle proteins (SMPs, water-insoluble) and soya proteins (SPs) at pH 12 prior to neutralization, the unfolding–folding pathways of both proteins were altered. Structural characterizations evidenced the complexation of SMPs and SPs using their secondary structures as the building blocks. Due to hydrophobic coalition between the α-helix (from SMPs) and β-sheet (from SPs), the co-assembled structures obtained considerable resistance against folding triggered by the hydrophobic effect. In addition, the kinetics by which the SMPs and SPs folded together was tailor-made by the compositional differences of the two proteins, resulting in the formation of well-defined, water-dispersible nanospheres with a tunable size and internal arrangements of the backbones. This study would enrich our choice of manipulated protein structures and enlarge the available protein sources with tailorable functions when applied in specific scenarios.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...