Cerebral effect of optimized Allium sativum oil-loaded chitosan nanorods: GC-MS analysis and in vitro/in vivo evaluation
Abstract
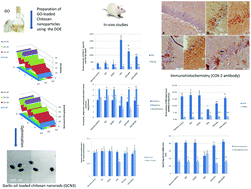
The chemical constituents of Allium sativum (garlic) oil were investigated using the GC/MS technique after silylation, and the presence of several fatty acids and their esters was revealed. The most dominant was 9,12-octadecadienoic acid (linoleic acid), a precursor of arachidonic acid, which is essential for brain development. Garlic oil-loaded chitosan nanoparticles (GCNs) were prepared to enhance its cerebral effects, and to mask its odor and taste. Two-level orthogonal factorial design, followed by regression analysis, was used to study the influence of different formulation variables. GCN3, the formula with the smallest particle size and the highest mucoadhesion, was selected as the optimized one. Transmission electron microscopy showed that GCN3 has a short nanorod-shape outline. We aimed to investigate the influence of orally administered GCN3 compared to the plain garlic oil (GO), on ciprofloxacin-induced (CPX) neurotoxicity in rats and the probable underlying mechanisms. The results show the significantly higher neurological curative effect of GCN3 compared to GO, and its greater antidepression-like and antianxiety-like potential via the alteration of brain neurotransmitter levels and inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammatory pathways. The histopathological examination showed the higher capability of GCN3 to repair the damage induced by CPX in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus area and substantia nigra brain sections. Similar results were proved immunohistochemically using Cox-2 antibody. The nanoencapsulation of GO represents a promising strategy for brain-targeting.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...