Adjunctive vitamin A and D during pulmonary tuberculosis treatment: a randomized controlled trial with a 2 × 2 factorial design
Abstract
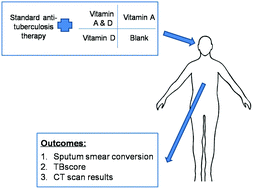
Background and objective: Vitamin A and D have immunoregulatory effects and may improve the response to pulmonary tuberculosis treatment. The interaction of vitamin A and D on pulmonary tuberculosis treatment has not been studied. The objective is to investigate the effects of adjunctive supplementation of vitamin A, D and their interaction on the outcome of pulmonary tuberculosis treatment, primarily time to sputum smear conversion. Methods: We conducted a randomized controlled trial with a 2 × 2 factorial design in Qingdao, China. Eight hundred patients were enrolled to receive standard pulmonary tuberculosis therapy alone (control), or together with vitamin A (2000 IU d−1), or vitamin D (400 IU d−1) or a combination of vitamin A (2000 IU d−1) and D (400 IU d−1) during the intensive-phase of pulmonary tuberculosis treatment. Results: 761 patients were included in the tuberculosis symptom analysis; 521 patients with positive baseline sputum smear results were included in the sputum smear analysis. The allocation to vitamin A or D did not significantly influence the time to sputum smear conversion [vitamin A: adjusted hazard ratio: 1.021, 95% CI: (0.821, 1.271); vitamin D: adjusted hazard ratio: 0.949, 95% CI: (0.760, 1.185)]. No significant interaction was observed between vitamin A and D supplementation (p = 0.660). Vitamin D supplementation significantly relieved the tuberculosis symptoms as indicated by decreased TBscore [mean difference: −0.2, 95% CI: (−0.4, 0)] in week 2 to 4. Conclusions: Adjunctive supplementation of vitamin A and/or D did not improve the time to smear conversion in pulmonary tuberculosis patients. However vitamin D supplementation significantly improved tuberculosis symptoms during the first month of pulmonary tuberculosis treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...