Formation, structural characterization, stability and in vitro bioaccessibility of 7,8-dihydroxyflavone loaded zein-/sophorolipid composite nanoparticles: effect of sophorolipid under two blending sequences†
Abstract
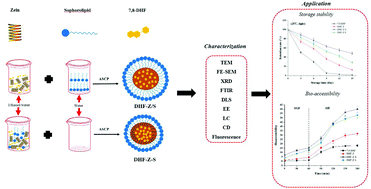
Anti-solvent co-precipitation (ASCP) is the most commonly used method of fabricating food-grade nanoparticles, while the impact of the blending sequence on the formation of nanoparticles lacks research. In this study, 7,8-dihydroxyflavone (7,8-DHF) loaded zein-/sophorolipid nanoparticles with two blending sequences (DHF-Z-S and DHF-Z/S) were successfully fabricated by the ASCP method and used to improve the storage stability and the in vitro bioaccessibility of 7,8-DHF. The results showed that blending sequences significantly affect the physicochemical properties of nanoparticles. DHF-Z-S nanoparticles had smaller particle size, lower polydispersity index and turbidity, and higher negative charge, entrapment efficiency and loading capacity compared to DHF-Z/S nanoparticles. Transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy revealed that DHF-Z-S and DHF-Z/S nanoparticles have core–shell spherical shape at the nanoscale and sophorolipid changed the surface morphology of zein nanoparticles. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and fluorescence spectrum analysis confirmed the presence of effective hydrogen bonding, electrostatic interactions and hydrophobic effects between 7,8-DHF, zein and sophorolipid and the presence of stronger hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic effects in DHF-Z-S nanoparticles. The encapsulated 7,8-DHF was in an amorphous state rather than a crystalline form as determined by X-ray diffraction analysis. Circular dichroism revealed that 7,8-DHF and sophorolipid were capable of changing the secondary structure of zein remarkably. More importantly, compared to DHF-Z/S nanoparticles, the DHF-Z-S nanoparticles possessed higher storage stability and in vitro bioaccessibility. Collectively, DHF-Z-S nanoparticles developed in this study might be a promising means of encapsulating, protecting and delivering hydrophobic nutraceuticals for applications in functional foods.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...