Lactic acid bacteria alleviate polycystic ovarian syndrome by regulating sex hormone related gut microbiota†
Abstract
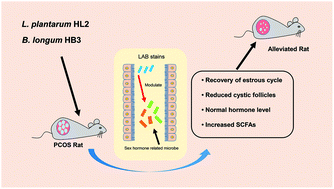
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrine disease across the world. Because gut microbiota play a key role in the pathogenesis of PCOS, probiotics may alleviate PCOS symptoms through the regulation of intestinal flora. The effects of 8 lactic acid bacterial strains on PCOS were investigated. Letrozole was used to produce a PCOS rat model and a 4-week-strain-intervention was performed. Diane-35, as a clinical PCOS treatment medicine, was effective in attenuating rats’ reproductive disorders. Lactobacillus plantarum HL2 was protective against ovary pathological changes and restored luteinizing hormone, follicle stimulating hormone and testosterone levels. Bifidobacterium longum HB3 also alleviated ovary abnormalities and decreased testosterone levels. Administration of lactic acid bacteria up-regulated short-chain fatty acid levels. Based on 16S rRNA sequencing, lactic acid bacteria improved letrozole induced gut microbiota dysbiosis with different degrees. Akkermansia, Roseburia, Prevotella, Staphylococcus and Lactobacillus genera were correlated with sex hormone levels. Some of the sex hormone-related gut microbiota were restored by treatment with the strains. These results demonstrated that lactic acid bacteria alleviated PCOS in a rat model by regulating sex hormone related gut microbiota. Modifying gut microbiota by probiotic interventions may thus be a promising therapeutic option for PCOS.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...