Exploring the flavor formation mechanism under osmotic conditions during soy sauce fermentation in Aspergillus oryzae by proteomic analysis†
Abstract
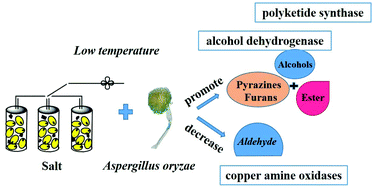
Aspergillus oryzae is a common starter in the soy sauce industry and struggles to grow under complex fermentation conditions. However, little is known about the flavor formation mechanism under osmotic conditions (low-temperature and high-salt) in A. oryzae. This work investigated the flavors and the relative protein expression patterns by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and proteomic analysis. Low-temperature and a high-salt content are unfavorable to the secretion of hydrolases and the formation of fragrant aldehydes. The aldehyde contents under osmotic conditions were reduced to 1.4–3.7 times lower than that of the control. Besides, copper amine oxidases which decreased under low-temperature stress and salt stress were shown to be important in catalyzing the oxidative deamination of several amine substrates to fragrant aldehydes. Furthermore, alcohol dehydrogenase and polyketide synthase are beneficial to the formation of alcohols and aromatic flavors under low-temperature stress and salt stress. Particularly, the ethanol content under 16 °C stress was 3.5 times higher than that under 28 °C.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...