In vitro growth performance, antioxidant activity and cell surface physiological characteristics of Pediococcus pentosaceus R1 and Lactobacillus fermentum R6 stressed at different NaCl concentrations
Abstract
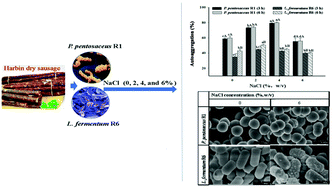
This study investigated the impact of NaCl concentrations on the growth performance, antioxidant activity, and cell surface physiological characteristics of Pediococcus pentosaceus R1 and Lactobacillus fermentum R6. The growth of the two strains was significantly inhibited by 4 and 6% NaCl and stagnated at 8% NaCl (P < 0.05). Compared with the control, both strains showed higher acid-producing activity, antioxidant activity and autoaggregation ability at 2 or 4% NaCl. A lower cell surface hydrophobicity of the two strains was observed with increased NaCl concentrations. High NaCl concentrations resulted in cell surface damage and deformation and even slowed the proliferation of the strains, and led to significant shifts in amide A and amide III groups in proteins and the C–H stretching of >CH2 in fatty acids (P < 0.05). In summary, appropriate NaCl concentrations (2 and 4%) improved the antioxidant activity of the two strains, while the higher NaCl concentrations (6%) decreased their antioxidant activity, which may be due to the associated changes in the cell surface structural properties of the two strains.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...