Microalgae aqueous extracts exert intestinal protective effects in Caco-2 cells and dextran sodium sulphate-induced mouse colitis†
Abstract
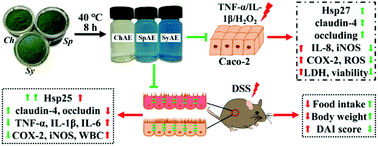
Microalgae are emerging as a good source of natural nutraceuticals. Here, we examined the intestinal protective effects of microalgae aqueous extracts (MAEs) from Chlorella pyrenoidosa, Spirulina platensis, and Synechococcus sp. PCC 7002 in human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells and dextran sodium sulphate (DSS)-induced colitis in C57BL/6 mice. MAEs displayed intestinal barrier-protective activities in Caco-2 cells by increasing the expression of heat shock protein (Hsp)-27 and tight junction proteins of occludin and claudin-4 and attenuating the H2O2-induced intracellular reactive oxygen species production, plasma membrane impairment and apoptosis. They also showed anti-inflammatory potential in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-, interleukin (IL)-1β- and H2O2-stimulated Caco-2 cells by suppressing the secretion of IL-8 and the expression of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS). The 8 d daily intragastric administration of MAEs during and after 4 d DSS exposure effectively alleviated colitis symptoms of weight loss, diarrhea, rectal bleeding, and colon shortening and histopathology, protected intestinal barrier function by increasing colonic Hsp-25, occludin and claudin-4, and attenuated colonic and systemic inflammation by suppressing colonic myeloperoxidase activity, production of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6, expression of COX-2 and iNOS, and peripheral leukocytosis, monocytosis and granulocytosis. Microalgae can thus serve as a functional food to maintain gut health.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...