Rice husk based nanocellulose scaffolds for highly efficient removal of heavy metal ions from contaminated water†
Abstract
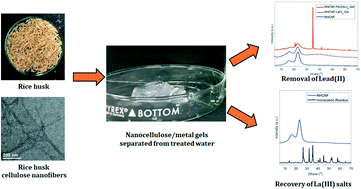
Rice husks are an agricultural residue of great annual production and have a high cellulose content. In this study, we have prepared highly charged carboxyl cellulose nanofibers (CNFs) from rice husks using the TEMPO-oxidation method and the extracted CNFs were evaluated as an adsorbent for the removal of lead(II) and lanthanum(III) (Pb(II) and La(III)) ions from contaminated water. Three different forms of nanocellulose adsorbents were prepared: suspension, freeze-dried, and nanocomposite containing magnetic nanoparticles, where their adsorption performance was tested against the removal of the two chosen heavy metal ions. The maximum adsorption capacity of rice husk based CNFs was found to be the highest in the nanocellulose suspension, i.e., 193.2 mg g−1 for Pb(II) and 100.7 mg g−1 for La(III). The separation of the used adsorbent in the suspension was further facilitated by the gelation of the CNFs and metal cations, where the resulting floc could be removed by gravity-driven filtration. The absorption mechanism of the investigated CNF system is mainly due to electrostatic interactions between negatively charged carboxylate groups and multivalent metal ions. It was found that 90% lanthanum content in the form of lanthanum oxychloride (determined by X-ray powder diffraction) could be obtained by incinerating the CNF/LaCl3 gel. This study demonstrates a viable and sustainable solution to upcycle agricultural residues into remediation nanomaterials for the removal and recovery of toxic heavy metal ions from contaminated water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...