Photocatalytic reductive defluorination of perfluorooctanoic acid in water under visible light irradiation: the role of electron donor†
Abstract
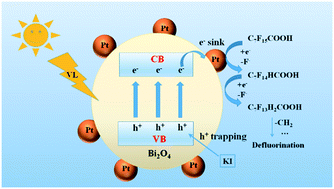
The development of efficient technology for perfluorooctanoic acid (PFOA) treatment has prompted much attention in water environmental fields, due to its global distribution and threats to ecosystems. In this study, a new method for reductive defluorination of PFOA under visible light (VL) was established by using Pt–Bi2O4 as a photocatalyst and KI as an electron donor. The defluorination process in water was found to occur via a photocatalytic reductive pathway, in which the photo-generated e− played the dominant role. The Pt served as a co-catalyst to trap the photo-generated e−, while KI could trap photo-generated h+ to suppress the undesired e−–h+ recombination, which cooperatively enhanced the defluorination efficiency. Along with PFOA reduction, very limited amounts of short-chain perfluorocarboxylic acid intermediates were generated, all of which could be further degraded to inorganic ions, and the total recovery of fluorine could reach 99% after 6 h of irradiation. The system also possesses high photostability, since the photocatalyst surface remained clean during the degradation. Finally, a decomposition pathway of stepwise removal of CF2 units was proposed in detail. As a proof-of-concept, the VL/Pt–Bi2O4/KI system not only shows potential for sustainable and “green” removal of PFOA in water, but may also find applications in the treatment of various refractory organic pollutants in water using solar energy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...