Impact of vacuum UV on natural and algal organic matter from cyanobacterial impacted waters†
Abstract
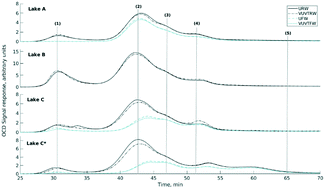
Cyanobacterial blooms are a growing concern around the world. A feasible approach for small treatment plants fed by sources contaminated with cyanobacteria is vacuum UV (VUV). VUV is a promising advanced oxidation process used to treat water impacted by cyanobacterial blooms, with potential applicability in small and remote communities because of its simplicity. In this work, water samples from three Canadian lakes periodically affected by cyanobacteria were used to assess the impact of natural and algal organic matter (NOM/AOM) on treatment with VUV. NOM and AOM were characterized before and after VUV treatment by size exclusion chromatography (SEC) and fluorescence emission–excitation matrix (FEEM). FEEM spectra were analyzed with the parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC) tool. As a result, we found seven principal components describing the whole dataset. Disinfection by-product (DBP) formation after VUV treatment was analyzed and trihalomethanes (THM) yield was calculated. THM yield increased by 15–20% after VUV treatment. Regarding DBP formation and NOM/AOM fractions from SEC, we found that humic substances are the most important fraction causing the increase in DBP formation with at least 3 times higher yield than the other fractions: biopolymers, building blocks, low weight molecular acids and neutrals.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...