Nanostructured manganese oxides exhibit facet-dependent oxidation capabilities†
Abstract
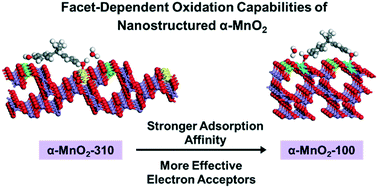
Applying nanostructured manganese oxides (nano-MnOx) in contaminated agricultural lands offers the coupled benefits of oxidizing a range of environmental contaminants while simultaneously releasing micronutrients (i.e., dissolved Mn2+) that are vital for crop growth. However, little is known about how the key nanocrystal properties affect the oxidation capabilities of nano-MnOx. Here, we show that an α-MnO2 nanostructure with predominantly exposed {100} facets (referred to as α-MnO2-100) exhibits greater oxidation capability for bisphenol A (BPA, a model pollutant commonly found in agricultural lands) than an α-MnO2 nanostructure with predominantly exposed {310} facets (α-MnO2-310), while consistently releasing a greater amount of Mn2+. Fitting the reaction kinetics data using a retarded rate model shows that α-MnO2-100 possesses more reactive sites with higher reactivity. Density functional theory (DFT) calculations show that the {100} facet possesses a higher density of binding sites and the complexation of BPA molecules on the facet is thermodynamically more favorable, mainly due to its specific surface topography. Moreover, ligand-promoted Mn(III) release experiments and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis verify that α-MnO2-100 contains a greater abundance of surface Mn(III), a more effective electron acceptor than Mn(IV). The findings suggest that facet engineering can be exploited to improve the performance of nano-MnOx for sustainable agricultural applications.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Environmental Remediation


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...