Effect of calcination temperature on neptunium dioxide microstructure and dissolution†
Abstract
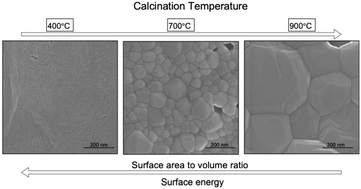
Comprehensive thermodynamic understanding of nuclear materials is paramount for long-term management of legacy nuclear waste and commercial spent nuclear fuel. Actinide oxides (AnO2(s)) are ubiquitous materials throughout the nuclear fuel cycle, yet existing thermodynamic data has noticeable discrepancies, creating uncertainty in environmental prediction of the fate of nuclear materials. The microstructure of actinide oxides, particularly neptunium (Np) and plutonium (Pu), is rarely investigated using high resolution electron microscopy, but such features may illuminate why differences in solubility measurements persist. The aim of this study was to synthesize NpO2(s) at varying calcination temperatures, characterize the materials using high resolution electron microscopy, and perform batch solubility studies to measure total dissolved Np as a function of calcination temperature. The current work demonstrates the sizable differences in dissolution of NpO2(s) based on process conditions, such as the temperature at which the material is calcined and resultant particle size, and the need for more thorough evaluation of the microstructure of solid phases used to generate thermodynamic data of actinides.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Environmental fate of nanomaterials


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
