UV-induced aggregation of polystyrene nanoplastics: effects of radicals, surface functional groups and electrolyte†
Abstract
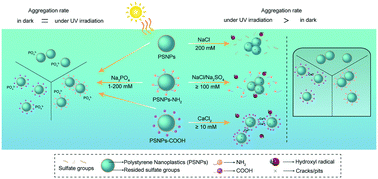
Aggregation behavior determines the fate and bioavailability of nanoparticles in aquatic environments. This study investigated the effect of UV irradiation and salts (NaCl, Na2SO4, CaCl2, and Na3PO4) on the aggregation of three polystyrene nanoparticles (PSNPs) with various surface functional groups. UV irradiation promoted the aggregation of pristine PSNPs in NaCl (>100 mM) and amino-modified PSNPs (PSNPs-NH2) in NaCl (≥100 mM) or Na2SO4 (≥100 mM) solutions. Under UV irradiation, hydroxyl radicals (˙OH) degraded the sulfate groups of PSNPs and amino groups of PSNPs-NH2 and decreased electrostatic repulsion forces among particles. Carboxyl-modified PSNPs (PSNPs-COOH) were relatively stable in NaCl and Na2SO4 solutions because of their high negative surface charge and hydrophilicity even after UV irradiation. Similarly, because the negative surface charge of PSNPs and PSNPs-NH2 in CaCl2 (1–50 mM) remained high under UV exposure, the strong electrostatic forces retarded the UV effect on the aggregation of PSNPs and PSNPs-NH2. However, UV irradiation accelerated PSNPs-COOH aggregation in CaCl2 (≥20 mM), probably because UV irradiation generated more carboxyl groups, which bind with Ca2+ and increase aggregation via a bridging effect. PO43− inhibited ˙OH photogeneration and stabilized the three types of PSNPs. Our study reveals the intriguing effects of light irradiation and salts on the aggregation behavior of emerging plastic nanoparticles in aquatic environments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...