Irradiation intensity dependent heterogeneous formation of sulfate and dissolution of ZnO nanoparticles†
Abstract
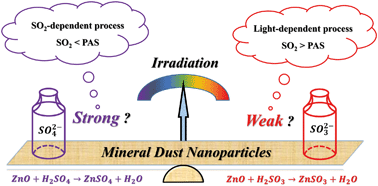
Atmospheric photochemistry is widely regarded as an important pathway for SO2 oxidation. The influence of irradiation intensity, especially photochemistry under weak sunlight during heavy haze events is not known. This work investigates the irradiation-intensity-dependence of the dust-related heterogeneous process using in situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS) and ex situ flow reaction. Illumination of the particles alters the surface oxygen species, and further accelerates the significant oxidation of sulfite species to sulfate products. The sulfate formation rate grows rapidly from the dark state to faint irradiation, while it becomes insensitive to irradiation intensity variation under strong illumination. According to the photo-electrochemical tests and concentration dependence experiments, this interesting phenomenon can be interpreted by the presence of excess SO2 under weak sunlight and sufficient photoinduced active species (PAS) under strong illumination. This uneven promotion effect is beneficial for explaining the sulfate burst under faint sunlight during heavy haze events. More significantly, the uptake of SO2 accounts for the increase of acidic species and the decrease of adsorbed water on the particle surface, thus elevating the particle acidity. Under these circumstances, the dissolution of zinc oxide (ZnO) takes place, and results in diverse principal products varying with the illumination condition, e.g. ZnSO3 under weak sunlight while ZnSO4 under strong irradiation. In general, photochemistry has profound impacts on atmospheric sulfur cycling, as well as the cycle of metal elements. The irradiation intensity dependent effects imply the raising uncertainty in the current air quality models.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...