Lateral size dependent colloidal stability of graphene oxide in water: impacts of protein properties and water chemistry†
Abstract
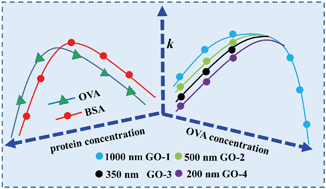
The effects of model proteins (OVA: ovalbumin and BSA: bovine serum albumin) on the colloidal stability of graphene oxide (GO) with different lateral sizes (around 1000, 500, 350 and 200 nm, respectively) were investigated. At low salt concentrations, the aggregation rate (k) of GO displayed a parabolic relationship: it increased until kfast (regime I), remained at kfast (regime II), and then decreased gradually to zero (regime III), with the increase of protein concentrations at environmental pH (4, 6 and 9). Compared to BSA, much higher concentrations of OVA were needed to achieve similar effects on GO stability induced by BSA, since OVA has a smaller molecular size and fewer positively charged groups. In regime I, the k of GO increased with the increase of lateral size at the same concentration of proteins, and a higher dosage of proteins was needed to drive k to kfast for smaller sized GO. However, there was no such lateral size dependent effect in regime III, which was attributed to the predominance of steric repulsion caused by the large amount of proteins. In regime I, GO displayed higher stability at higher pH, and thus more proteins were required to drive k to kfast. In regime III, the proteins were more effective in stabilizing GO under higher pH conditions due to the enhanced electrostatic and steric repulsion. This study highlights the crucial effects of the GO lateral size, protein properties and concentrations, as well as solution chemistry, on GO stability in aquatic environments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...