Diverse dechlorinators and dechlorination genes enriched through amendment of chlorinated natural organic matter fractions†
Abstract
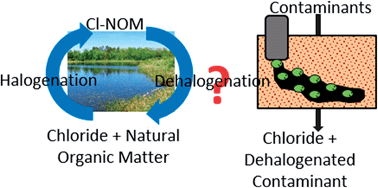
In uncontaminated environments, chlorinated natural organic matter (Cl-NOM) can act as an electron acceptor for organohalide-respiring bacteria. It is unknown, however, whether different types of Cl-NOM are preferentially dechlorinated or whether enrichment with Cl-NOM affects the ability of bacteria to dechlorinate contaminants. In this research NOM was extracted from sediment, fractionated based on hydrophobicity, and either amended to polychlorinated biphenyl-contaminated soil directly or chlorinated and then amended to soil. Amendments of the least hydrophobic Cl-NOM fraction were dechlorinated most rapidly, followed by the moderately hydrophobic Cl-NOM fraction. Soil that had been enriched on the moderately hydrophobic fraction of Cl-NOM was also capable of faster dechlorination of the contaminants trichloroethene and tetrachlorobenzene. Community analysis of the soil during enrichment showed that some known organohalide-respiring bacteria were present and may have played a role in dechlorination; nevertheless, many bacteria appeared to be enriched during both Cl-NOM and contaminant dechlorination. In addition, the quantities of two haloalkane dehalogenase genes increased during enrichment on Cl-NOM. These results show for the first time that Cl-NOM can prime contaminant dechlorination and also suggest that hydrolytic dechlorination processes were involved in both Cl-NOM and contaminant dechlorination.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Halogenated (semi)volatile organic compounds (“X(S)VOCs”)


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...