Identification of water-infiltration-induced electrical energy generation by ionovoltaic effect in porous CuO nanowire films†
Abstract
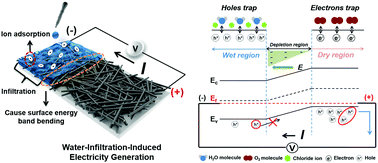
We verified the origin of water-infiltration-induced electricity generation by an ionovoltaic effect, specifically, ion–surface interaction induced potential asymmetry in porous structures. When 20 μl of water (NaCl, 0.1 M) infiltrates into a porous CuO nanowire film, electrical power of ∼0.45 V and ∼0.23 μA is produced for 40 minutes. Moreover, a method of proportionally amplifying electricity is presented, and the practicability is shown by turning on an LED with infiltration of eight seawater droplets.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...